Firms can pay dividends in periods in which they incurred losses, provided retained earnings and the cash position justify the dividend. And in some states, companies can declare dividends from current earnings despite an accumulated deficit. The financial advisability of declaring a dividend depends on the cash position of the corporation. A stock dividend is when a company issues additional shares of its own stock to its shareholders, usually in proportion to the number of shares they already hold. The value of the dividend is determined by the current market price of the stock.
Dividend declaration date
Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications. At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website.
Accounting for a stock dividend
As soon as the dividend has been declared, the liability needs to be recorded in the books of account as dividends payable. On the initial date when a dividend to shareholders is formally declared, the company’s retained earnings account is debited for the dividend amount while the dividends payable account is credited by the same amount. As the payment date approaches, the company prepares to disburse the dividends to its shareholders. On the payment date, the company will need to settle the liability recorded earlier. This is done by debiting the Dividends Payable account and crediting the Cash account. This entry effectively reduces the company’s cash balance, as the funds are transferred to the shareholders, and eliminates the liability that was previously recorded.
Unit 14: Stockholders’ Equity, Earnings and Dividends
In this case, the company may pay dividends quarterly, semiannually, annually, or at other times (either fixed or not fixed). Cumulative preferred stock is preferred stock for which the right to receive a basic dividend accumulates if the dividend is not paid. Record the declaration and payment of the stock dividend using journal entries. It is useful to note that the record date is the date the company determines the ownership of the shares for the dividend payment. Like in the example above, there is no journal entry required on the record date at all. For example, on December 14, 2020, the company ABC declares a cash dividend of $0.5 per share to its shareholders with the record date of December 31, 2020.
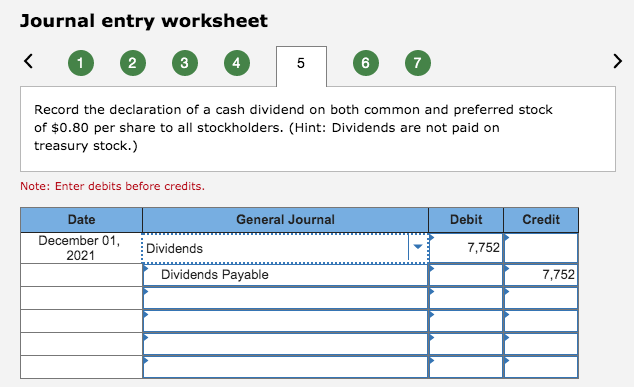
Dividend declared journal entry
In this situation, the date the liability will be recorded in Your Co.’s books is March 1 — the date of the Board’s original declaration. Applying Generally Accepted Accounting Procedures (GAAP), which is required for any public company and a good practice for private companies, means recording tax deductible pregnancy medical expenses the dividend when it is incurred. To be a Dividend Champion, a stock must have paid rising dividends for 25+ consecutive years. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements.
Journal Entries for Dividend Payments
Companies often offer shares at a discount through DRIPs, making them an attractive option for shareholders. However, it’s important to note that reinvested dividends are still subject to taxation, as shareholders must report the value of the reinvested dividends as income on their tax returns. This tax treatment underscores the importance of understanding the financial and tax implications of participating in a DRIP. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate financial reporting and analysis. The primary types of dividends include cash dividends, stock dividends, and property dividends.
This type of dividend does not result in a cash outflow but does affect the components of shareholders’ equity. When a stock dividend is declared, the retained earnings account is debited for the fair value of the additional shares to be issued. Upon distribution, the common stock dividend distributable account is debited, and the common stock account is credited, reflecting the issuance of new shares. Stock dividends dilute the ownership percentage but do not change the total value of equity held by each shareholder. They are often used when companies wish to reward shareholders without reducing cash reserves.
The debit to dividends payable reduces the liability on the company’s balance sheet, as the obligation to pay dividends is being settled. The credit to the cash account reflects the outflow of cash from the company to its shareholders. This entry finalizes the transaction and the dividends payable account should be brought to zero, indicating that all declared dividends have been paid. It is crucial for the company to ensure that the cash account has sufficient funds to cover the dividend payment, as failure to do so could result in financial distress or legal issues. A small stock dividend occurs when a stock dividend distribution is less than 25% of the total outstanding shares based on the shares outstanding prior to the dividend distribution.
- And of course, dividends needed to be declared first before it can be distributed or paid out.
- Investors who purchase shares after the date of record but before the payment date are not entitled to receive dividends since they did not own the stock on the date of record.
- Both small and large stock dividends occur when a company distributes additional shares of stock to existing stockholders.
- Stock investors are typically driven by two factors—a desire to earn income in the form of dividends and a desire to benefit from the growth in the value of their investment.
The declaration of dividends is a signal to the market, often interpreted as a sign of a company’s strong financial health and future earnings prospects. On the payment date of dividends, the company needs to make the journal entry by debiting dividends payable account and crediting cash account. While a company technically has no control over its common stock price, a stock’s market value is often affected by a stock split. When a split occurs, the market value per share is reduced to balance the increase in the number of outstanding shares. In a 2-for-1 split, for example, the value per share typically will be reduced by half.

Dividends are typically paid in cash, but they can also be distributed in the form of additional shares of stock or other investments. It is at that time that the dividend becomes a liability of the corporation and is recorded in its books. Since there are 100,000 common shares outstanding, the total cash dividends will be $120,000. Once the previously declared cash dividends are distributed, the following entries are made on the date of payment. Later, on the date when the previously declared dividend is actually distributed in cash to shareholders, the payables account would be debited whereas the cash account is credited.
The difference is the 3,000 additional shares of the stock dividend distribution. The company still has the same total value of assets, so its value does not change at the time a stock distribution occurs. The increase in the number of outstanding shares does not dilute the value of the shares held by the existing shareholders. The market value of the original shares plus the newly issued shares is the same as the market value of the original shares before the stock dividend.
